Southern California Edison Model 120: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|neigh = 2 (Rotor) 10 (Blower) | |neigh = 2 (Rotor) 10 (Blower) | ||
}} | }} | ||
The SoCal Edison (SCE) 120 or Model 120 was a | The SoCal Edison (SCE) 120 or Model 120 was a 120 dB low tone pneumatic siren designed in house by Southern California Edison for use within the 10 Mile Emergency Planning Zone (EPZ) for the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS). | ||
== Origins == | |||
There were 22 of these sirens produced with one being never installed which is now privately owned. 16 were installed in July 1983 to add into a system of 32 Federal Signal STL-10s that were installed in April 1982 with 2 of the STL-10s being swapped out for Model 120s, and later in 1988 5 additional locations were installed one of which replacing a Thunderbolt that was actually a CD siren used by one of the cities before SONGS took over it for use in their siren system. The reason these sirens were made is because there was no other siren available that would meet the plants needs. The only sirens that were available on the market that have the range the plant was looking for were rotating directional sirens only, of which the plant wanted Omnidirectional only sirens. They did look into ACA Cyclones which was the most powerful omnidirectional siren available, but they realized it didn't have the coverage the plant wanted being about 3,000 or so feet less then the plants range requirement, and the fact that they have massive 50 Hp motors which was overkill for a siren with such a range of only about 4,000ish feet. The other reason is because the STL-10s underperformed in all areas they were placed in, as well as federal lying to SoCal Edison about the STL-10 being 120 decibels and having the specific effective range that the plant required (which was about 6,000 or more feet effective range) to cover the EPZ due to the hilly terrain of the jurisdictions in the EPZ. | |||
| Line 18: | Line 22: | ||
[[File: | [[File:7 Model 120 heads and blowers.jpeg|thumbnail|7 Model 120 heads and Paxton blowers prior to being assembled.]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:Assembled unit without horns.jpeg|thumbnail|Unit assembled without Horns attached.]] | ||
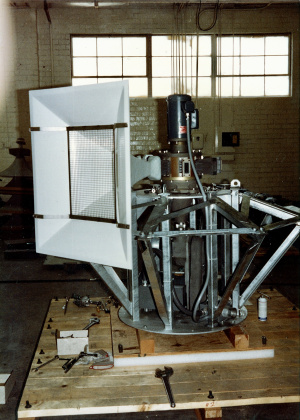
[[File: | [[File:Horns being attached and conduits ran to main junction box.jpeg|thumbnail|Horns beginning to be bolted up and conduits from both motors ran to the main junction box for incoming power.]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:5 out of the 8 horns attached with another unit being assembled off to the left.jpeg|thumbnail|5 out of the 8 horns bolted up with another unit being assembled off to the left. (NOTE: the additional parts on the shelves for units later installed which was another batch of 7 about a few months later).]] | ||
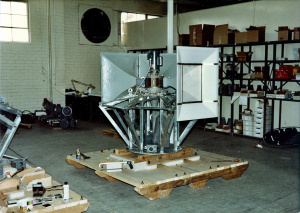
[[File: | [[File:Closer view of the head with the siren 95% assembled.jpeg|thumbnail|Closer view of the head with the siren 95% assembled.]] | ||
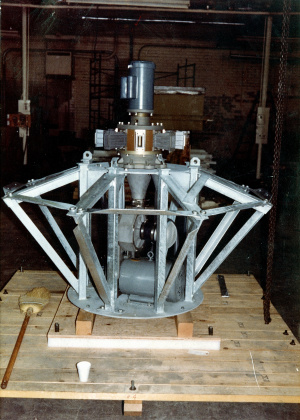
[[File: | [[File:Fully assembled Model 120.jpeg|thumbnail|Unit after being assembled.]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:Fully assembled Model 120 with the other 6 being assembled and crated up to be transported to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station for installation in the 10 mile EPZ around May-June 1983.jpeg|thumbnail|Fully assembled Model 120 with the other 6 being assembled and crated up to be transported to San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station for installation in the 10 mile EPZ. These were the first batch to be installed with another batch of 7 a month or two later, along with a final batch of 7 by 1988 bringing the total number of sirens to 21.]] | ||
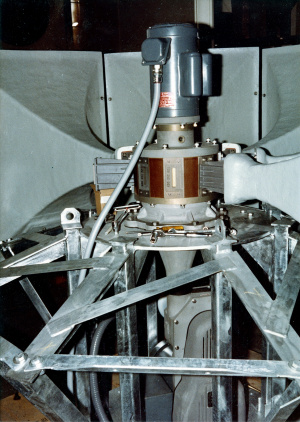
[[File: | [[File:99F6BBFC-E550-4A8C-8538-82E2356B663A.jpeg|thumbnail|Rotor and stator of the privately owned unit with a motor attached. As you can see it looks exactly the same as the unit in the photo above, just without the horns and frame assembly. The motor is not the exact same motor as the other ones that were installed, but is the same rating, Horsepower, and RPMs.]] | ||
== See Also == | |||
* Siren patent: https://patents.google.com/patent/US4649853 | |||
[[Category:SoCal Edison]][[Category:Omnidirectional Sirens]][[Category:Pnuematic Sirens]][[Category:Single Toned Sirens]][[Category:Sirens]] | [[Category:SoCal Edison]][[Category:Omnidirectional Sirens]][[Category:Pnuematic Sirens]][[Category:Single Toned Sirens]][[Category:Sirens]] | ||
Revision as of 06:22, 18 January 2022
| Southern California Edison Model 120 | |
[[File: |200px]] |200px]]
| |
| Company | Southern California Edison |
|---|---|
| Produced | 1983 and 1988 |
| Type | Pneumatic |
| Sound output | 120 |
The SoCal Edison (SCE) 120 or Model 120 was a 120 dB low tone pneumatic siren designed in house by Southern California Edison for use within the 10 Mile Emergency Planning Zone (EPZ) for the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS).
Origins
There were 22 of these sirens produced with one being never installed which is now privately owned. 16 were installed in July 1983 to add into a system of 32 Federal Signal STL-10s that were installed in April 1982 with 2 of the STL-10s being swapped out for Model 120s, and later in 1988 5 additional locations were installed one of which replacing a Thunderbolt that was actually a CD siren used by one of the cities before SONGS took over it for use in their siren system. The reason these sirens were made is because there was no other siren available that would meet the plants needs. The only sirens that were available on the market that have the range the plant was looking for were rotating directional sirens only, of which the plant wanted Omnidirectional only sirens. They did look into ACA Cyclones which was the most powerful omnidirectional siren available, but they realized it didn't have the coverage the plant wanted being about 3,000 or so feet less then the plants range requirement, and the fact that they have massive 50 Hp motors which was overkill for a siren with such a range of only about 4,000ish feet. The other reason is because the STL-10s underperformed in all areas they were placed in, as well as federal lying to SoCal Edison about the STL-10 being 120 decibels and having the specific effective range that the plant required (which was about 6,000 or more feet effective range) to cover the EPZ due to the hilly terrain of the jurisdictions in the EPZ.
So starting in around June 1982, Model 120 prototypes started to be constructed and tested, with the final designed units being completed in March 1983, and the first 16 installed in July 1983, and later on 5 more in 1988 to cover new housing and business development in a part of the city of San Clemente that was being constructed around 1987 bringing the total to 21 Model 120s and a total number of 52 sirens with the already existing 32 STL-10s.
Originally the plan was after the Model 120s were installed, a now total of 52 sirens were going to be all Model 120s which means swapping out the existing 32 STL-10s with 120s making the system Model 120's only, but this plan was dropped shortly afterwards and only about 8 Model 120s ended up swapping out STL-10s with the other ones being new locations that didn't replace STL-10s. This was due to the whole siren thing causing delays to the plant by not having a ready siren system by 1981 which was the original year for the plants 2 new reactors that just finished construction, Units #2 and #3 to begin operation, but due to the STL-10s originally bought not meeting the plants needs by not effectively covering the EPZ, they had to find another siren that meets the plants needs in order for the plants new reactors to start operations which caused a delay for over a year, this also happened around the same time the NRC required Nuclear plants to have siren systems, but until SONGS get sirens that can perfectly cover the 10 mile EPZ, the plants new reactors could not begin operations, and the plants original reactor that was the first reactor to be built in 1968 (Decommissioned in 1992 and completely demolished by 2006) Unit #1 could not be restarted until the siren system is fully operational and effectively covers the EPZ. So after the Model 120s went up, to end the delays of the siren system not being up to par, which costed over $1 million per day that held up the plant from starting, it was decided to just keep the underperforming STL-10s and just add 21 Model 120s in areas that need coverage to get the EPZ effectiveness up to code for the plants original reactor to restart, and the new reactors to start. After a successful system test around late July 1983, the plants new reactors began operation shortly afterwards with Unit #2 starting on August 8th, 1983, and Unit #3 on April 1st, 1984, as well as Unit #1 restarted.
For around a decade, they were thought to be "Toshiba" sirens, because they were pneumatic and people just assumed they were made by Toshiba, who also made pneumatic sirens. The Model 120 is a Pneumatic siren, meaning it requires an external air source to produce sound. The sound is chopped by a rotor, which sits inside a hollow cylinder, or stator, which acts as a chamber to contain the air inside. 8 Small narrow slots on the stator allow the sound to come out. The sound is then projected by 8 large fiberglass horns. It consists of a belt driven Paxton blower, that uses a 10 Hp TEFC motor. The rotor is 9.75 inches in diameter and has 5 ports. Including the stator it is in total 11.75 inches in diameter. The rotor is powered by a 2 Hp TEFC motor that spins at 3600 RPM. By 6/10/2004, the plant was discussing a system replacement project due to saying the current system is "aging", and a year later starting In November 2005, (a month after the annual siren test), the Model 120s and the STL-10s started to be gradually removed and replaced, and by Febuary 2006 all have been replaced marking October 26th, 2005 as the final test of the original system, as well as the end of the one of a kind original system that stood out from all other Nuclear plant systems. Whelen WPS 2810s and WPS 2806s were installed in their places. The 2810s went in place of the Model 120s and the 2806s went in place of the STL-10s. These new electronic sirens have battery backup, are more efficient, less maintenance, and having similar ranges to the original system such as the 2806s having better range compared to the STL-10s, and the 2810s having close to the same range but about 2,000 feet less range compared to the the Model 120, but still enough range to cover the EPZ, and as for the strict requirements of the original system, that was no longer an issue as by the 2000s there was commercially produced omnidirectional sirens that have close to the same range as the Model 120 and as well have better range then the STL-10s. After all the old sirens have been removed and replaced, SONGS sold 23 of the STL-10s to Curry County Oregon to be used as tsunami sirens, and the Model 120s and remaining 5 STL-10s are believed to have been scrapped, but its unknown if they were, or went somewhere else but hasn't been discovered. The only Model 120 that is known and remaining is in the possession of Aaron Allevato (Duderocks5539) and Edaan Friedman and currently under restoration to be brought back into operating condition.




See Also
- Siren patent: https://patents.google.com/patent/US4649853